Risk of missing gigabit connectivity for all target by 2030, leaving tens of millions of people behind
Europe has reached record levels of telecom investment, progressing on both 5G and FTTH coverage. New estimates show the European Union looks likely to miss its gigabit-for-all-by-2030 target by 10%.
Those new estimates are some of the findings of ETNO’s report, the State of Digital Communications, which is based on research by Analysys Mason, published just as the European Commission is expected to launch a public consultation on the future of the telecom sector and its ability to invest in new networks.
Gigabit targets, global competitiveness
Despite the highest level of investment in telecoms infrastructure since 2016, Europe risks missing the Digital Decade target of gigabit connectivity for all, even if operators can keep up current record levels of investment in the face of high interest rates and possible economic downturn.
Projections suggest that very high-speed networks are on track to reach about 90% of EU citizens by 2030, potentially leaving tens of millions of Europeans behind.
In 2021, the total telecom CapEx reached a whopping €56.3 billion in Europe compared with around €1 billion invested by Big Tech, for instance in international and undersea routes, peering, transit and caching, and €16 billion in data centres.
At the end of 2022, 55.6% of the European population had access to FTTH networks, up from 50% in 2021. Similarly, 5G is now available to 73% of Europeans, up from 62% the previous year.
Lagging global peers
Yet Europe lags global peers: at the end of 2022, 5G coverage of the population reached 96% in the US, 95% in South Korea, 90% in Japan and 86% in China.
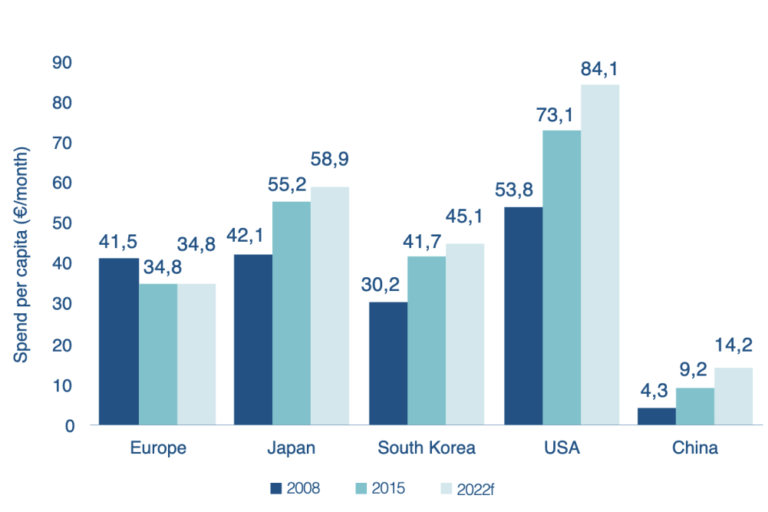
Europe is also behind all global peers on investment per capita adjusted to GDP: Europe invested €104.4 per capita in 2021, compared to €259.7 in Japan, €149.6 in the US and €110.2 in China (see graph at top of article).
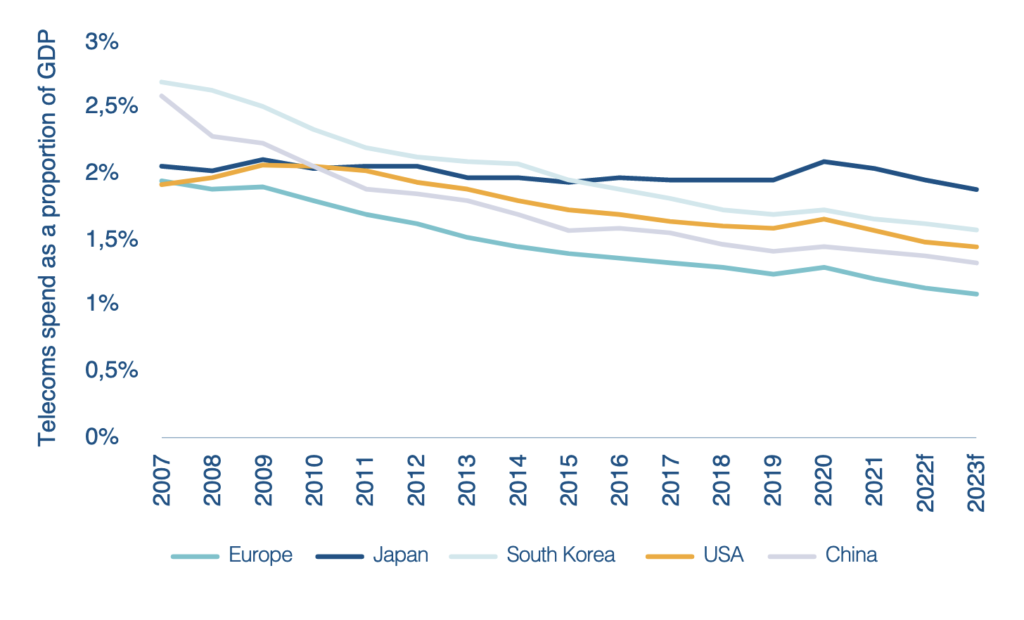
Whereas Europe was formerly much more in harmony with other regions on its investment per capita, interesting, as shown below, it has remained the lowest spend as a proporation of GDP since 2017. Presumably the two are related.
Jury out on edge cloud, 5GSA , Open RAN
According to the research, Europe counted 18 edge cloud offers in 2022, second only to Asia-Pacific with 19 offers, and performing better than North America, with five.
When it comes to Open RAN Europe had six trials underway in 2022, the same number as China, followed by the US and South Korea with three each, and Japan with two.
However, on the implementation side, the most significant Open RAN deployments are Japan’s Rakuten Mobile and in the US’s DISH Networks.
By the end of 2022, Europe had increased the number of 5G Standalone networks to four, compared to three the previous year but the Asia-Pacific region had 15 networks and North America three.
Fundamentally weak
Europe’s telecom shares consistently underperform peers on the stock market, as they have since 2018: the Stoxx Europe 600 index has performed worse than the Global 1900 for telecoms, but also than the shares of major tech companies.
At the same time, the European telecom sector is in a phase of very high capital investment and its debt is also rising. In 2021, the share of revenues re-invested was nearing 20%, while the debt/EBITDA ratio of ETNO members was at 2.53, the highest level since 2014.
Sustainability
Telcos are greening their own networks and enabling other sectors to achieve green targets through digital networks and services. Some 83% of the energy used by telecom companies in 2021 derived from renewable sources, up from 71% in 2018.
European operators’ scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions per revenue have more than halved over time: from 5.11 CO2e in 2017 to 2.18 CO2e in 2021.
The transition to more efficient networks like FTTH and 5G is bringing about plans to decommission less green legacy networks: between 2023 and 2024, ETNO expects 10 fixed networks to be decommissioned per year and 36 2G and 3G networks to be decommissioned in 2023 and 41 in 2024.
Rupert Wood, Research Director, Analysys Mason commented, “The continuing poor health of the telecoms sector works against Europeans’ interest. Poor returns make the infrastructure investment needed to achieve the 2030 Digital Decade targets more challenging, and they dent hopes of a renaissance of innovation and skills in new digital communications technologies”.