Keeping track of service and network assets has never been easy writes Markus Buchner, Director of Product Management, Amdocs.
As with operations support systems (OSS), inventories used to be set up for each new service or technology. Now the arrival of highly dynamic technologies like virtualization, cloud, edge, Network as a Service and 5G is making it even harder to keep tabs on network and service resources.
Rather than replace siloed inventories and consolidate copious amounts of data on physical, logical and virtual network resources, an alternative solution is inventory federation. Federation brings together data from existing data sources, providing centralized visibility and control over all assets and their increasingly complex interdependencies.
These capabilities are vital for end-to-end service and network orchestration, itself a ‘must have’ to support end-to-end lifecycle management in emerging multi-layered networks.
The question is not whether to implement inventory federation, but how best to go about it. Let’s look at the three fundamental approaches.
3 approaches to inventory federation
The choice of inventory federation depends on the use case, the required performance and the data volumes to be extracted, reconciled and analyzed.
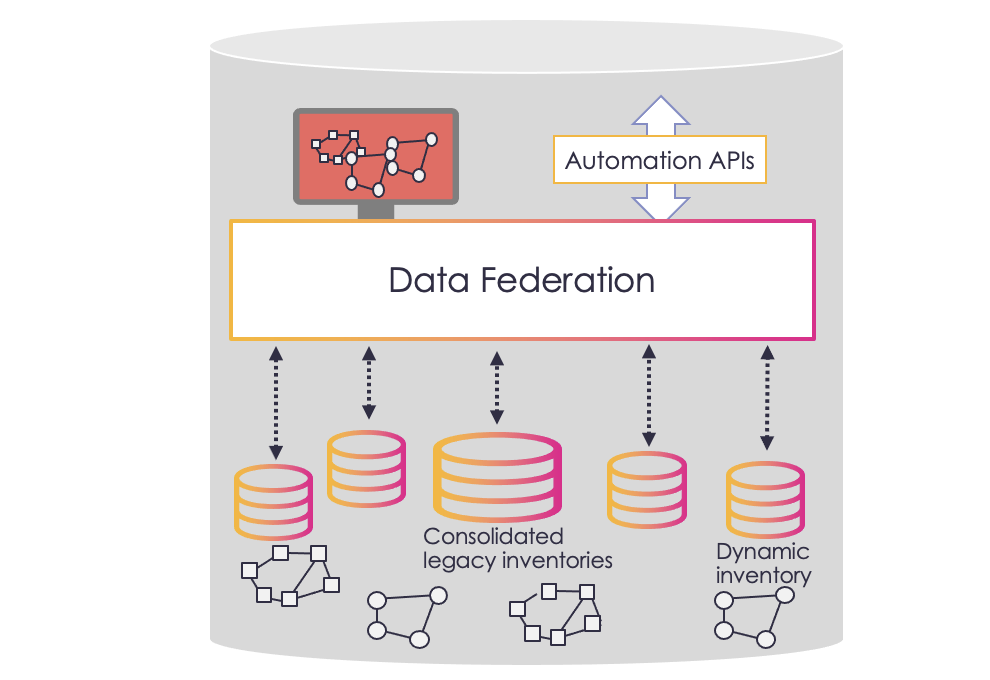
The first approach is real-time federation – for dynamic network domains, live data needs to be extracted on-demand from multiple inventory data sources. For example, when a fault occurs, a service assurance application may need to analyze a range of network topology data to perform a root cause analysis. Federation must bring these data sources together in real time so that faults can be identified and resolved quickly.
For less dynamic network and service data, replication is an option. Replication involves extracting information from multiple master data sources into a single datastore or ‘cache’. Data is extracted in a recurring reconciliation cycle, typically from one to four times a day, or updated through event-driven mechanisms. Data queries are then run against this ‘offline’ dataset.
Replication is used when data query performance and responsiveness is critical. It is best suited to relatively static source data and where a range of data points are needed to answer the underlying query.
There is a third federation approach – data enrichment. This is where most of the data comes from a single master inventory database, but critical information from other systems is added in real time.
An example is the insertion of the real-time error count of an optical link from a network management system into the relevant network element record in the inventory database. This makes the record useful to a wider range of operations personnel, such as service assurance teams.
Choosing the mix of federation approaches
The key criteria regarding which approach to apply to a business scenario are:
• The frequency, volume of data queries and required response times for the federated inventory;
• The necessity for true real-time as opposed to near real-time or even off-line data;
• The completeness of data that needs to be exposed – all inventory data or just a subset?
• The relative criticality of the master data sources’ native processes compared to those running on the federated inventory – is there a need to prioritize or avoid negative impact?
• The directionality of the federation flows required – just ‘READ’ or READ/ WRITE?
Typically, a mix of all three federation approaches – real-time, replication and data enrichment – will be used in parallel, due to the wide variety of use cases that require federated network data.
Mastering federation challenges
In addition to choosing the right federation approaches, CSPs also need a supporting federation infrastructure that can reconcile a variety of data labels and formats.
This is because different inventories typically hold some of the same data – but in different formats and using different labelling conventions.
For example, gateway nodes that connect network domains are likely to appear in both the core and edge domain inventories. One inventory may refer to the ‘location’ of the node, the other may call it the ‘site’ of the node. The federation platform needs be able to map, merge and deduplicate such data held under different labels.
Conversely, unique information about a network element may be spread across multiple inventory databases. For example, data about a router may comprise core facing and edge facing sides, each of which is managed in a separate inventory system. The federation platform must be capable of merging all that data into easily consumable records.
Federation case studies
Given the complexity of balancing the challenges and priorities, how do CSPs juggle them in the real world?
A European tier 1 service provider chose a replication approach to inventory federation for service assurance, adding Amdocs’ real-time data grab mechanisms for unified access to network data across network towers.
A cable MSO in North America has deployed Amdocs’ solution for mapping, merging and replicating network data sources to accelerate service fulfillment and network fault resolution.
Another North American tier 1 CSP is using a federated data enrichment strategy for service and network automation, adding physical network information to enrich SD-WAN and virtualized network inventory data.
Enabling inventory federation to pivot
Inventory federation is a big step in the evolution towards network data management, especially when taking into account the increasing number of data sources and the sheer volume of network and service data created.
CSPs must be able to flexibly combine federation approaches as their networks and business needs evolve. The underlying federation platforms must support all three approaches to enable coverage of the full range of use cases.
Real-time federation and data enrichment are key to a future-ready OSS, in particular to support end-to-end network and service orchestration and assurance which rely on a real-time view of dynamic network and service data across network domains.
Find out more here:
Modernize your inventory whitepaper
Amdocs Open Network Inventory