Telefónica, up six places, is the biggest mover in Juniper Research’s ranking
The Global IoT Roaming Market 2023-2028 study by Juniper Research predicts there will be more than 600 million roaming IoT connections by 2028, up from 145 million in 2023. However, it notes that this growth depends on the implementation of new roaming standards to detect and monetise IoT roaming. In July, Juniper Research predicted that by 5G IoT Roaming connections will reach 142 million by 2027, up from 15 million in 2023. This will equate to 27% of all 5G roaming connections in four years’ time.
Juniper’s new report identified billing and charging evolution (BCE) as a critical technology in allowing operators to identify new roaming connections to drive growth. In turn, this will allow operators to maximise inbound roaming revenue.
The research analysed how comprehensive 18 IoT players’ IoT services are (see graphic below), as well as their innovation levels and future prospects. The top five, in descending order, are Vodafone Roaming Services, Telefónica, Tata Communications, TNS and BICS. You can see last year’s ranking here.
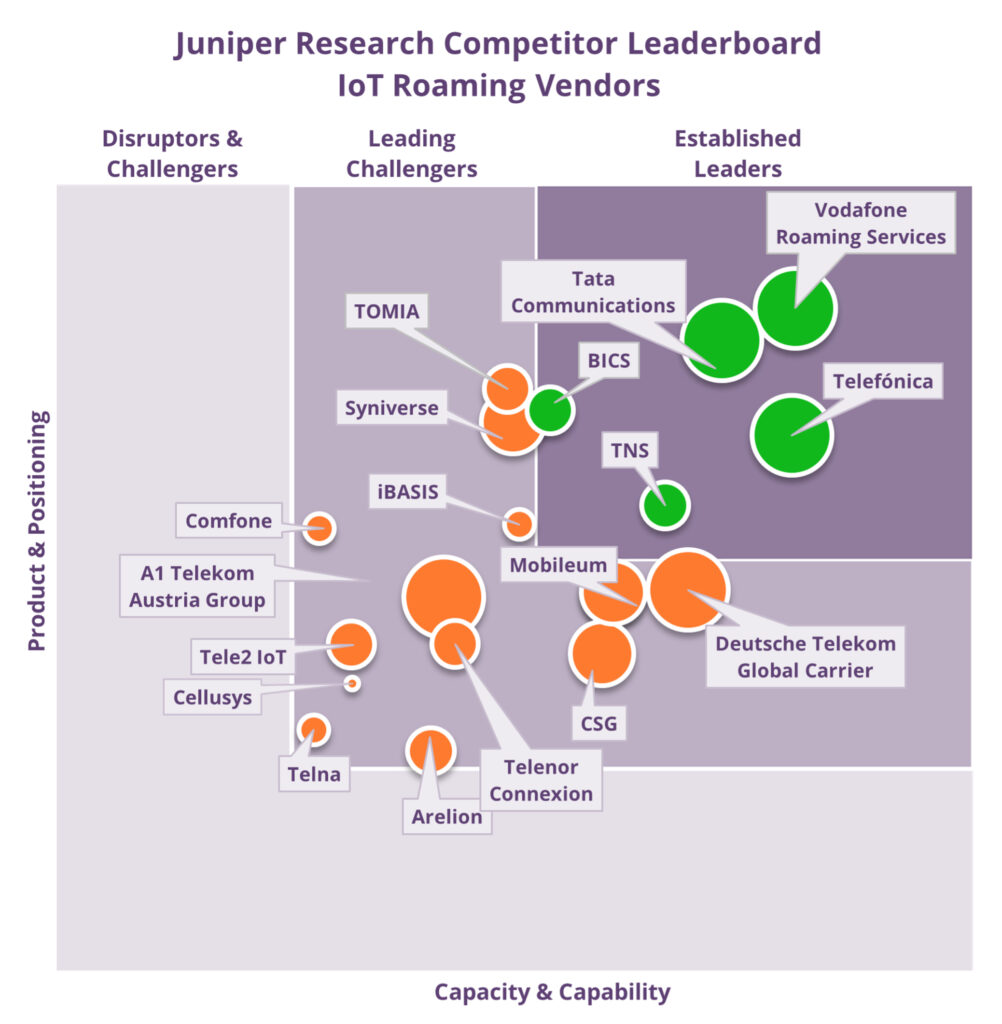
Vodafone keeps its crown
Juniper says that maintained its top ranking Vodafone Roaming Services’ in large part due to the expansion of its global IoT roaming network. The operator also has a comprehensive portfolio of IoT management solutions as well as “significant” coverage put Vodafone Roaming Services as in poll position as the vendor to enable operators to maximise future inbound roaming revenue.
Telefónica is the big mover in 2023
Telefónica has risen six places in the ranking, driven by its innovative solutions that simplify monetising IoT roaming. For example, the company has continued to innovate with BCE, and services to help operators manage different roaming regulations.
The coming eSIM revolution
A recent blog by Mohit Agrawal of Counterpoint identified the lack of permanent roaming as a major issue. IoT roaming uses cellular connectivity across geographic locations for extended periods to support applications such as logistics, remote monitoring and agriculture, among other things. In contrast, roaming that travellers and their smartphones use is temporary.
The problem is, some of the world’s biggest economies have placed limitations on permanent roaming for IoT, as shown below. These 12 countries collectively account for more than 50% of the world’s population.
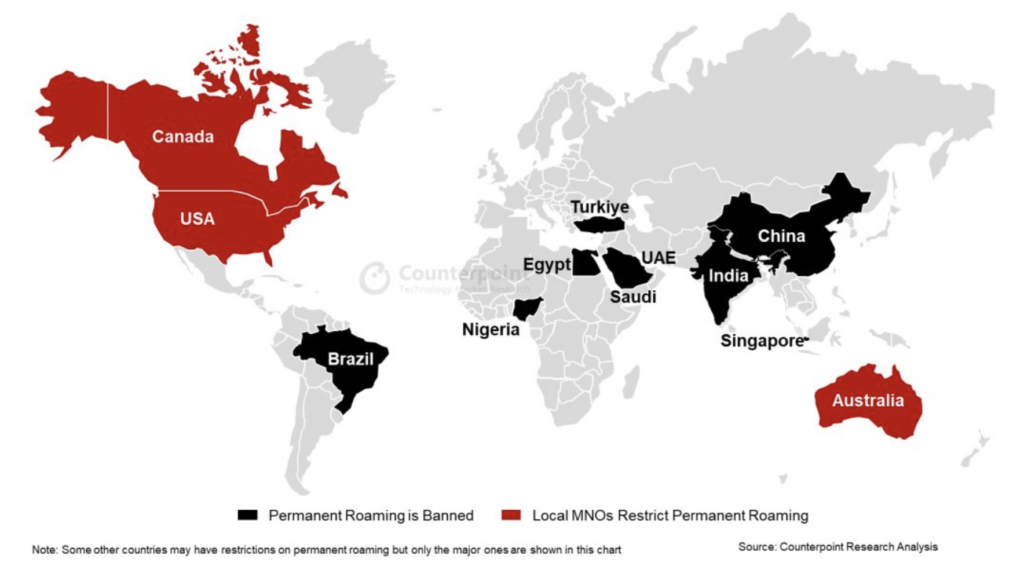
Source: Counterpoint
This is why eSIM is expected to have a huge impact as IoT devices with eSIMs can be remotely provisioned over the air instead of having to physically replace SIM cards. eSIM will allow IoT roaming vendors to switch between a local profile and multiple roaming profiles every 90 days according to the blog, thereby avoiding contravention of permanent roaming rules.
It will be interesting to see how much the implementation of eSIM affects Juniper Research’s rankings for roaming IoT in 2024, although Counterpoint stresses that other innovations, such as international multi-subscriber identity and aggregator platforms also have a role to play.


