New survey by Enea, the Swedish data management specialist for mobile operators, finds many children spent hours online unsupervised during lockdowns.
As operators race to roll out new specialised services for those working from home for companies big and small, another need has become clear.
A survey commissioned by Enea, conducted last month by Censuswide, found that many children are left unsupervised online during lockdowns for extended periods.
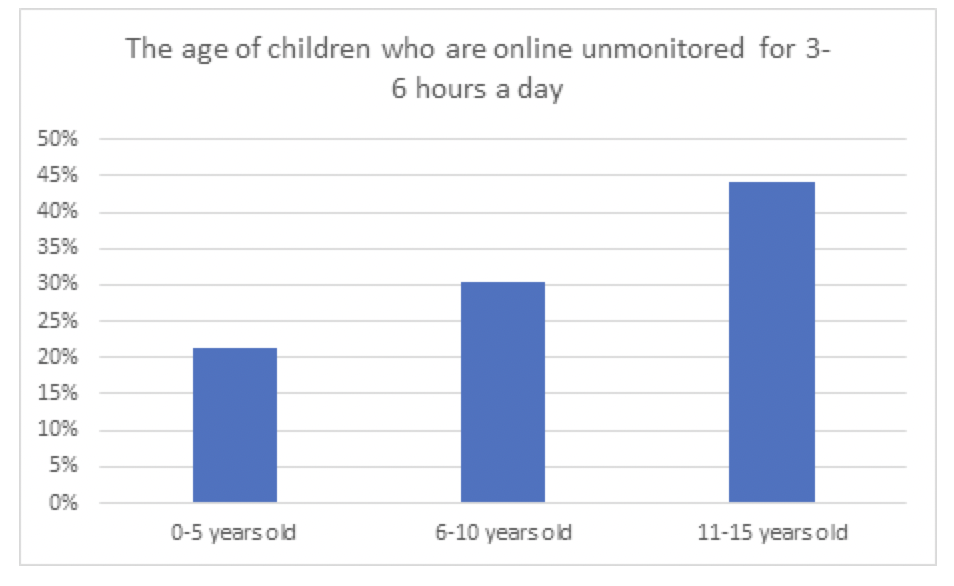
Unsupervised mobile activity was a challenge for parents of children of all ages: 44% of 11 to 15-year-olds and 30% of 6 to 10-year-olds spent three to six hours a day unmonitored. Even parents of children under five revealed their offspring spent at least an hour a day unsupervised on a mobile device.
Enea interviewed 4,000 households in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the UK and US about children’s mobile internet use last month.
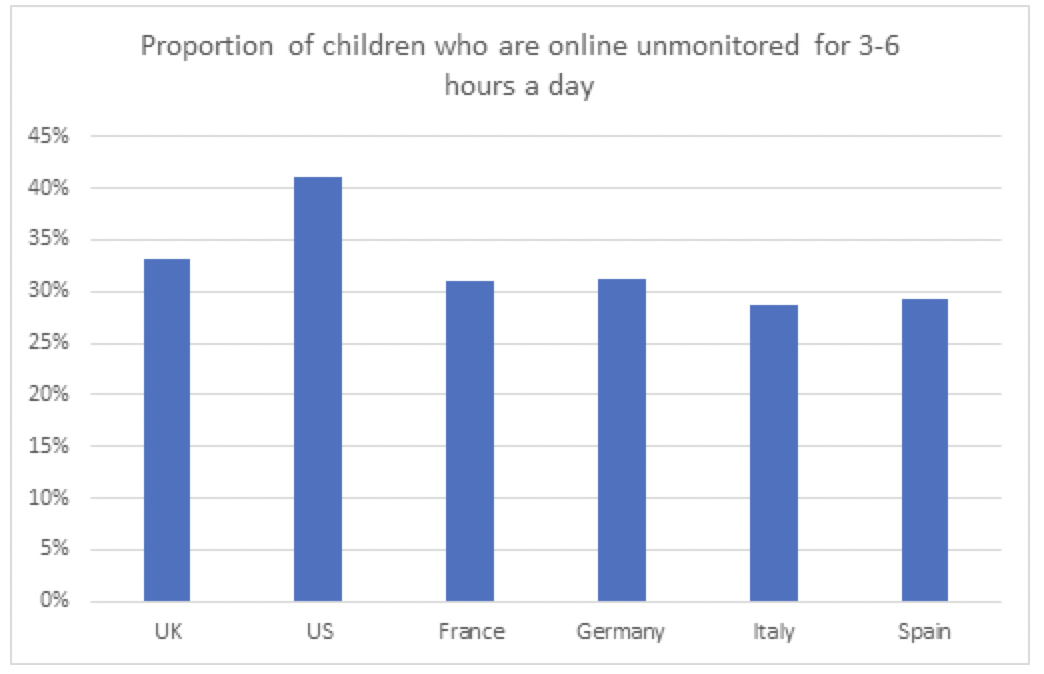
The survey highlights concerned parents who are looking for effective safeguards for their children while they are accessing the internet via mobile devices. The challenge appears to be most acute in the US where children spent the most amount of unsupervised time online.
Whom to trust?
When parents were asked who they trust to safeguard children online, eight our of 10 parents said they would welcome help with parental controls from mobile operators. By contrast, less than a quarter of all parents said they would trust Facebook, Google or any other social media provider with their children’s online safety.
Indranil Chatterjee, Chief Customer Officer at Enea, said, “We all know the internet…has its dangers. It’s clear that parents overwhelmingly trust mobile operators to support them, in contrast to other big tech players. And that means operators not only have a responsibility – they also have a commercial opportunity – to strengthen their safeguards for children.”
Parents willing to pay
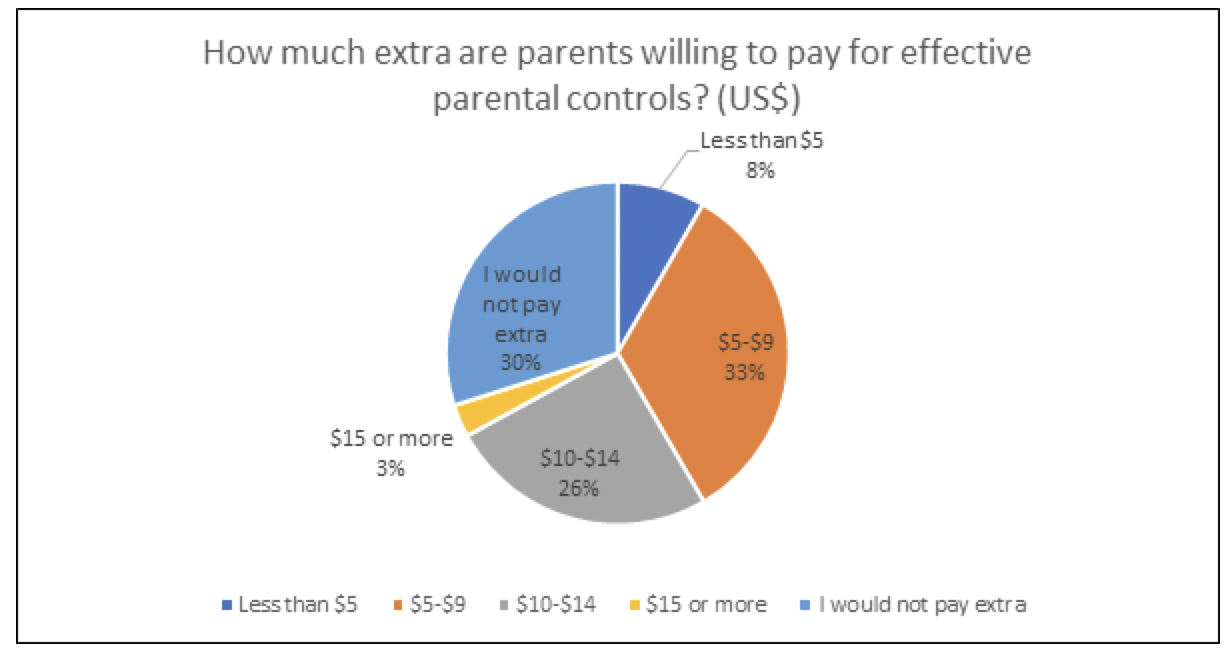
Further, parents are willing to pay. Some 58% of parents said they would willingly pay an additional $5 to $14 (€4 to €11.45) per month for more effective safeguard controls for their children.
UPDATE to clarify: The survey also asked if respondents would leave their mobile operator if it didn’t offer parental control for one that did at did for a similar monthly fee? Over half (56%) of parents said they would.
Parental control is difficult
One of the issues facing providers of content filtering and parental controls is high levels of encryption.
Gorkem Yigit, Principal Analyst, Analysys Mason, commented, “Encryption protocols such as HTTPS and QUIC have made it more challenging for operators to stop inappropriate content such as adult, gambling or violence reaching vulnerable users.
“And things could get worse later this year as existing parental control solutions could be rendered obsolete due to the growing adoption of [Transport Layer Security] TLS 1.3 with encrypted SNI [server name indication] that will blind-side operators. So, to effectively safeguard children, operators should consider deploying AI-based traffic classification systems that can instantly identify content based on statistical prediction, behavioral analysis and heuristics.”












