Sponsored: How wired and wireless deployments take advantage of lithium-ion batteries by JD DiGiacomandrea
Lithium-ion batteries are well known to be smaller and lighter, enabling portable devices to shrink and run longer. Now why would stationary applications, where space and weight are rarely an issue, benefit from a lithium-ion battery? Lithium-ion batteries have more benefits than just size and weight. These benefits include lower costs, higher reliability, increased flexibility, and remote monitoring. Wireless Network operators are finding these benefits fit their needs and are deploying more lithium-ion batteries than ever before.
The advantages of lithium-ion batteries often make them a more practical option for UPS backup power, especially in small-scale and remote deployments.
Reliable power
The failure of lithium-ion batteries in UPS applications is extremely rare. Today’s battery providers utilize quality materials, superior design, and improved manufacturing methods to produce lithium-ion batteries that are built for reliability in all kinds of mission-critical environments. Research and investment in EV lithium-ion batteries has spilled over and benefits all lithium-ion batteries. Battery management systems (BMS) have evolved and improved over the past 20 years. These advanced BMS paired with modern cells create highly reliable backup batteries, as well as add monitoring, and advanced algorithms to monitor health of the cells.
Energy density & faster recharge
Lithium-ion batteries have a higher power density (watts per kilogram, or W/Kg) and energy density (watt hours per kilogram, or Wh/Kg) than lead acid batteries. They provide the same amount of energy in a lighter, more compact design. There are a few sub chemistries to choose from, as shown in Figure 1.
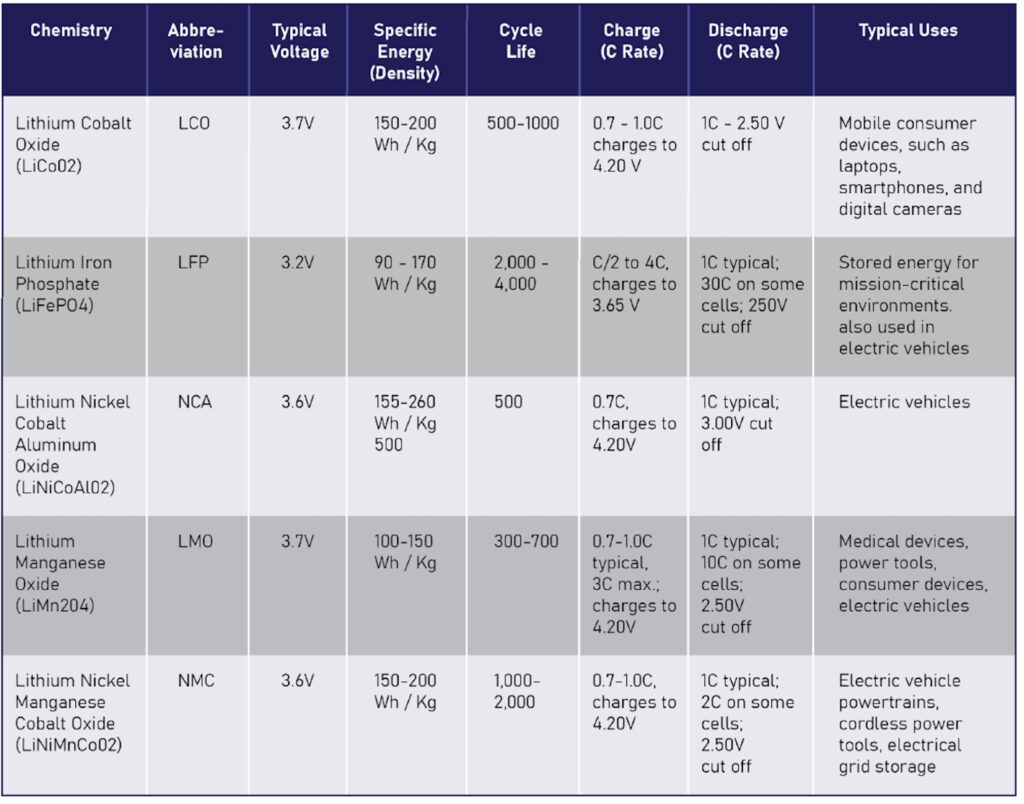
Also, most lithium-ion batteries can be recharged over 90% capacity in under two hours, while VRLA batteries may take anywhere from four to 24 hours to fully recharge. If an edge data center or 5G cell station has multiple utility outages in a single day, the lithium-ion batteries can quickly be recharged to provide ride-through time for each outage. Additionally, Lithium-Ion batteries can be paired with Solar, Wind, or fossil fuel generators to charge quickly and discharge slowly, optimizing energy harvesting when it is available.
Extended lifespan & cycle life
Lithium-ion batteries have a lifespan of 10-15 years, which is 2-3 times as long as the average 5-7 year lifespan of lead acid batteries. A lithium-ion battery may easily last the entire 15-year lifespan of your UPS. Also, lithium-ion batteries have a predictable degradation curve, which makes it easier to determine when they are approaching “end of life” and will need to be replaced; unlike lead acid batteries, aging lithium-ion batteries are not subject to “sudden death syndrome.” Additionally, you can discharge lithium-ion batteries from 100% to 0%, which is twice the available capacity of lead acid batteries without doing any damage to the cells at all!
Smaller size and lower weight
Lithium-ion batteries are up to 70% more compact than lead acid batteries. The smaller size of lithium-ion batteries makes it easier to install them in space-constrained deployments, such as modular or containerized data centers, 5G micro nodes, and data closets.
Also, lithium-ion batteries typically weigh about 1/3 less than most VRLA batteries. The lower weight makes lithium-ion batteries easier to carry, transport, and install, especially when delivering them to remote locations. Just talk to an installer, their knees and backs will thank you!
Temperature tolerance
In outdoor settings, lithium-ion batteries can tolerate higher (and lower!) ambient temperatures, and are less susceptible to sudden temperature changes that would shorten a lead acid battery’s useful life. In indoor settings, lithium-ion batteries provide a savings in cooling costs, since server rooms and data closets can be kept at a higher ambient temperature without fear of damaging the batteries.
Less maintenance
All lithium-ion batteries have a built-in Battery Management System (BMS) that monitors battery performance, reducing the risk of sudden battery failure. The BMS provides automatic status and fault monitoring, cell balancing, and power optimization for each individual battery.
A well-designed lithium-ion battery is virtually maintenance free, making it a “set it and forget it” solution. The BMS allows technicians to monitor battery health, in either a local or remote deployment. This allows you to maximize battery life, minimize downtime, and reduce labor and maintenance costs.
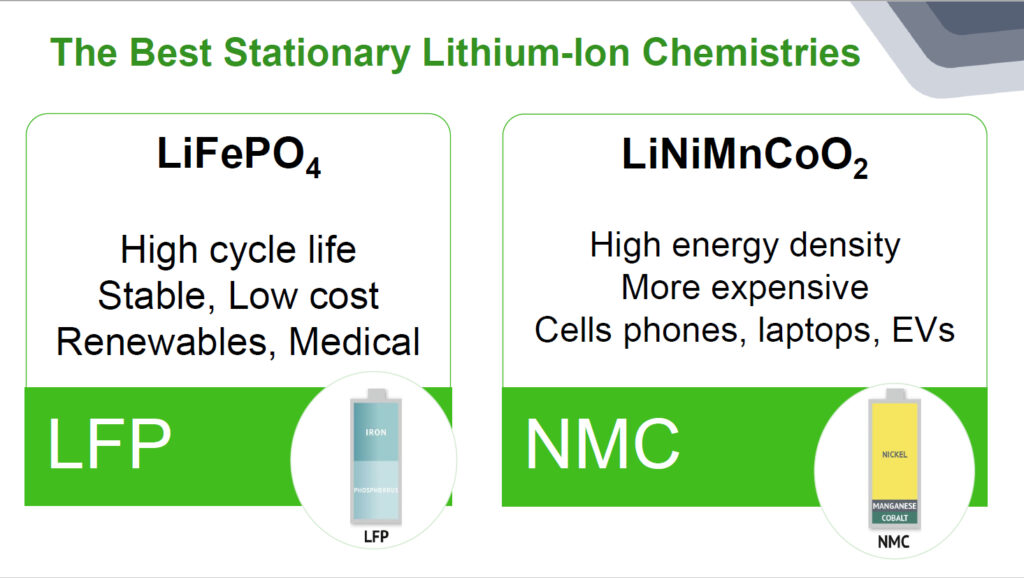
Cost comparisons – lithium-ion vs. lead acid batteries
Although the costs have decreased significantly over the last decade, lithium-ion batteries can require a higher initial investment than lead acid batteries. However, depending on the costs of the application, lithium-ion batteries offer long-term savings in Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) when used in 5G and IT network deployments. Figure 3 shows some of the categories to consider when selecting a backup power chemistry for your long-term deployment. Each deployment is different, but stationary battery applications typically operate for very long periods, many more than 15 years.
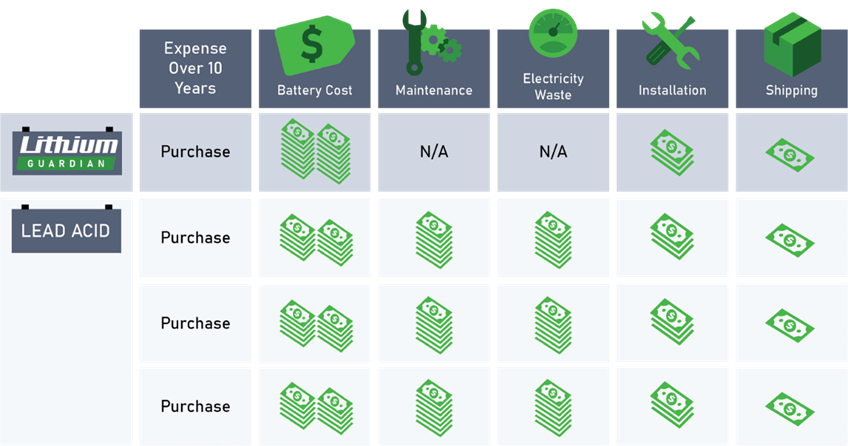
As mentioned, the longer lifespan and reliability of lithium-ion batteries means that they may last for the entire life of your UPS. This eliminates the cost of replacing batteries every few years, and also provides potential savings in labor, maintenance, shipping, and transportation that would otherwise be needed to service and replace the batteries in remote locations.
All in all, lithium-ion batteries benefits for stationary applications are at a tipping point. Many network operators are considering lithium-ion batteries as a cost saving, higher performing alternative to the traditional valve regulated lead acid batteries they are used to using. Is it time to consider usinglithium-ion batteries to back up your mission critical loads?


